If you’ve noticed that your internet is slow on your computer but fine on your phone, and both are actually on the same Wi-Fi network, it can sometimes be really confusing because you might think there is no way your phone can perform faster than your computer. In this guide, we’re going to look at why this happens and how to fix it.
Also see: Change Ethernet from 100Mbps to 1Gbps in Windows 11/10

Page Contents
See if there are any hardware limitations
First, think about your computer and phone’s hardware. Older computers might not be cut out for fast internet, but newer phones usually (and surprisingly) are.
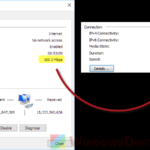
Network card
Your computer’s network card could be too old or not working right. If it was made ten years ago, it won’t keep up with new Wi-Fi speeds.
Think about updating your network card drivers or even getting a new network card that meets the latest Wi-Fi 6 standards.
Ethernet cables
If you use an Ethernet cable, its quality and type could affect your speed.

Make sure to use at least a Cat 5e cable. If that doesn’t help, try a new cable.
Linked issue: Ethernet Internet Speed Capped at 100 Mbps (Fix)
Software conflicts and background activity
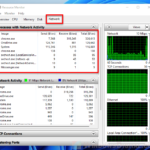
Software on your computer can slow down your internet speed. PCs run many different types of software that could use your internet without you knowing.
Background applications
Apps running in the background can use a lot of internet. This includes automatic updates and cloud services, and sometimes even malware.
Check for these using your computer’s task manager. On Windows, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc, then click the “Network” column to see what’s using your internet. On macOS, use the “Activity Monitor” and check the “Network” tab.
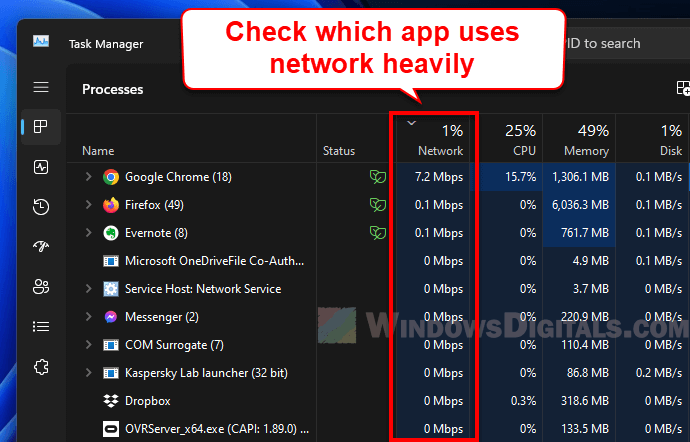
Close any tasks that you don’t need running.
Pro tip: How to Know Which App is Using The Internet in Windows 11
Browser extensions and add-ons (if any)
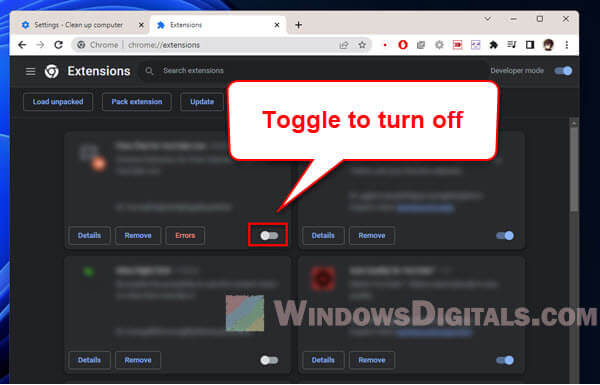
Some browser extensions can slow down your internet by loading extra data or running background tasks.
Try turning off extensions one by one to see if your speed improves.
Wi-Fi interference and how you place it
Where you place your computer and your router can affect your Wi-Fi speed.
Distance and maybe obstacles
Wi-Fi signals get weaker with distance and can be blocked by walls and other things. Your phone might be getting better speed because it’s usually closer to the router.
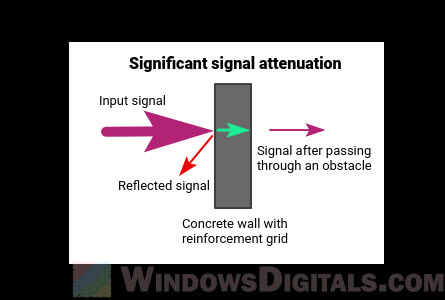
Try moving your computer closer to your Wi-Fi router or clear the path between them. You might also think about getting a Wi-Fi extender.
Related resource: Router to Modem/PC Auto-Negotiation at 100Mbps (not 1Gbps)
Interference from other devices
Devices like microwaves and cordless phones can mess with your Wi-Fi. This might affect your computer more than your phone.
Keep other devices away from your Wi-Fi router and your computer, or turn them off if you’re not using them.
Your network configuration and settings
Your PC’s settings might be causing slow internet speeds. Here’s how to fix them:
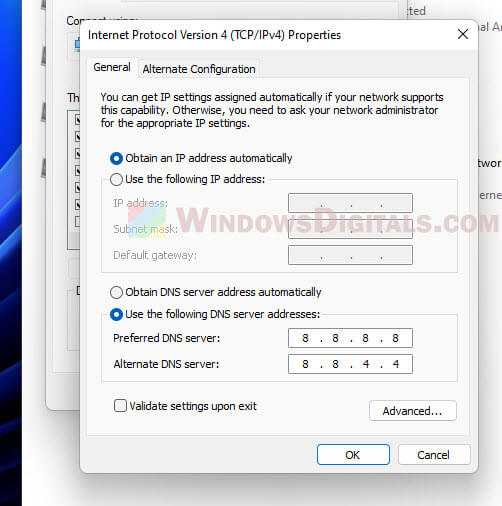
DNS settings
If your computer is using a slow DNS server, it can make websites slow to load.
Switch to a faster DNS server like Google’s (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare’s (1.1.1.1). You can do this in your computer’s network settings.
Learn more: DNS Servers to Unblock Websites and Possibly Everything
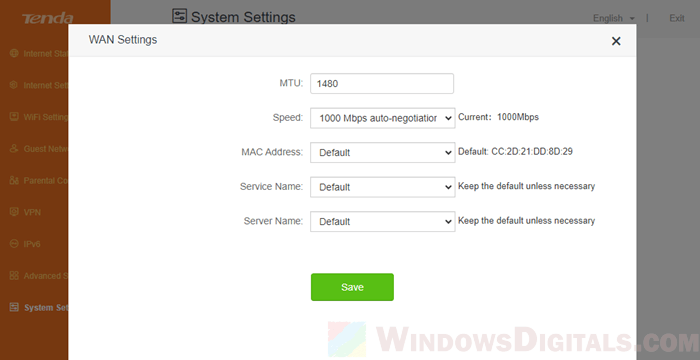
MTU might be incorrect
The right MTU size is important for fast data transmission. If it’s set wrong, it could slow things down.
Try changing your MTU size in your network settings or your router. The usual setting is 1500 bytes, but you might need to experiment.
Your OS and driver updates
Old operating systems or drivers can make your internet slow.
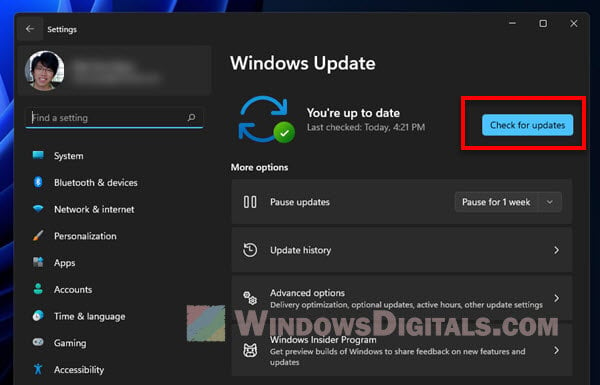
Outdated operating system
Make sure your operating system is up to date. For Windows, check in “Settings” > “Update & Security”. For macOS, go to “System Preferences” > “Software Update”.
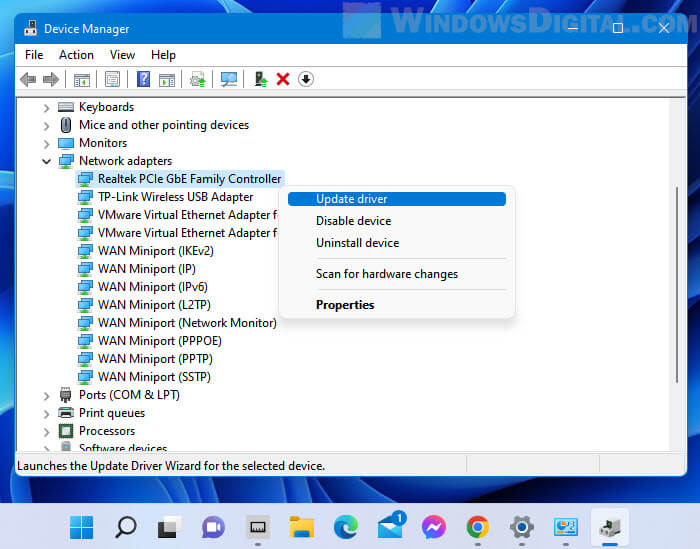
Outdated or incompatible drivers
Old or wrong drivers can also slow down your internet. Make sure your drivers are up to date. You can find new drivers on the manufacturer’s website or update them through your computer’s Device Manager. On macOS, updates usually include driver updates.
Suggested read: How to Update Realtek Drivers in Windows 11
Frequently asked questions
While we’ve covered a lot in this guide, you might still have some questions. Below are some answers that might help.
Why is my internet slow only on my desktop?
If you’re only having issues with your desktop, it could be because of an old network card, a bad Ethernet cable if you’re not on Wi-Fi, or an outdated operating system. Check the hardware and software tips we mentioned earlier.
Is it possible that my router is prioritizing my phone over my computer?
Yes, some routers can set priorities for different devices, which might make your computer slower. Check your router’s settings to see if this is happening, and adjust if necessary.
Can a VPN slow down my computer’s internet speed?
VPNs can make your internet slower because they encrypt your data and send it through a longer route. If your computer is much slower, try turning off the VPN to see if it helps. If you need a VPN for safety, look for one that is known for being fast, or only use it when you need to.