If you often use Google Chrome on either Windows 11 or Windows 10, you might have seen that your Task Manager shows many Chrome instances running, even if you’ve got just one tab open. This might make you worry about your computer working too hard, but actually, it’s totally fine.
In this article, we’ll talk about why you see many Chrome processes and how to handle the high CPU, memory, or disk use they might cause.
Page Contents
What are multiple Chrome instances in Task Manager?
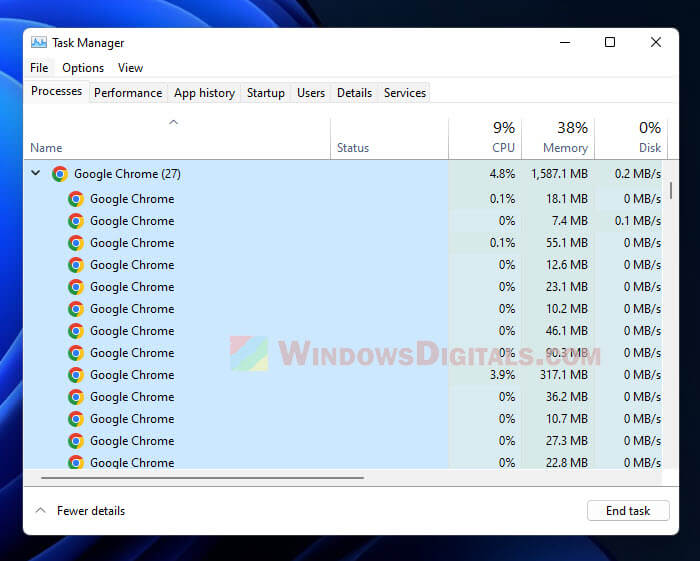
If you check the Task Manager while Google Chrome is on, you might notice lots of chrome.exe processes. These are different Chrome instances, each doing its own thing with its own bit of memory and resources.
Each one handles a part of Chrome, like showing websites, running extensions, or dealing with online stuff.
Suggested tip: How to limit CPU usage of a process in Windows 11
Why does Google Chrome run multiple processes?
The main reason Chrome does this is to make sure it works well, fast, and safely. By putting each tab, plugin, and extension in its own process, if one crashes or freezes, it doesn’t mess up everything else. You can just close what’s not working without losing everything.
This setup also lets Chrome work faster by using modern computers’ multiple cores better and keeps things safer. Each process is in its own “sandbox,” so bad stuff in one can’t spread to the others.
Related issue: Game lag when watching YouTube or Twitch on Chrome
Do the chrome.exe processes in Task Manager represent tabs I have opened in Chrome?
It’s easy to think each chrome.exe process is for each Chrome tab, but it’s not just that.
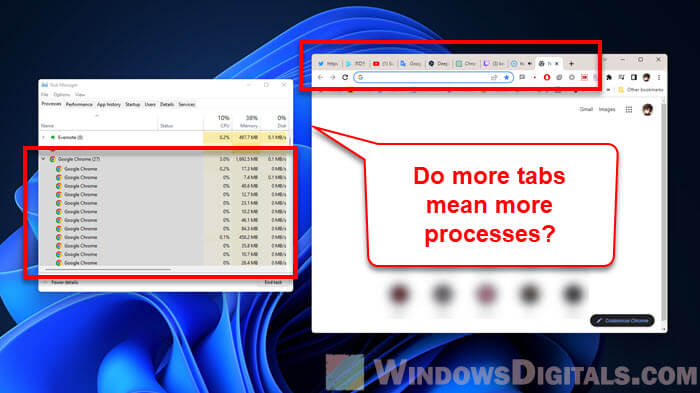
Alongside each tab, Chrome runs other necessary processes for the browser to work well, like the main browser process, graphics, webpage rendering, and utility tasks.
See also: High GPU usage while watching YouTube videos
Even with no tabs open, these processes keep running to make sure Chrome works smoothly.
What does multiple Chrome instances mean for my computer’s performance?
Having many Chrome instances can affect your computer, especially if it’s not very powerful. Every process uses some CPU and RAM, which can slow things down.
But, Chrome is made to use resources wisely to keep running well. Usually, you won’t notice much of a difference in performance.
Similar problem: Chrome Software Reporter Tool high CPU and disk usage
How can I reduce the number of Chrome processes?
Close unused tabs
Closing tabs you’re not using can help cut down on running instances. This saves memory and CPU, possibly making your computer faster. To close a tab, just click the “X” on the tab.
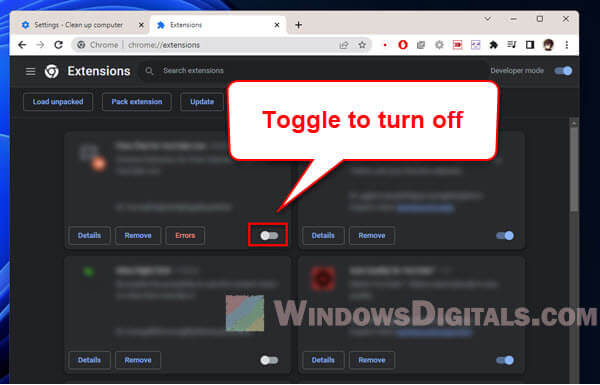
Remove unused and resource-intensive extensions
Extensions can also run their own processes. Getting rid of ones you don’t need or that use a lot of resources can help.
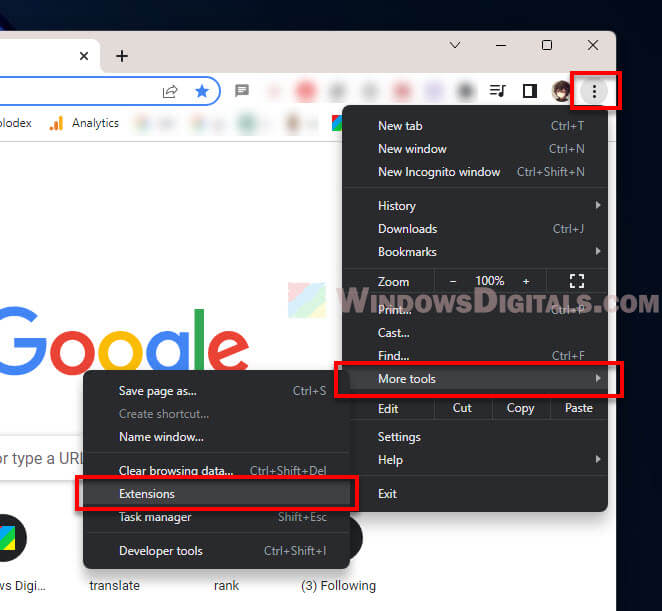
You can remove or disable extensions by doing this:
- Click on the three-dot menu in Chrome.
- Select “More Tools” > “Extensions“.
- Click on “Remove” or turn off the extension.
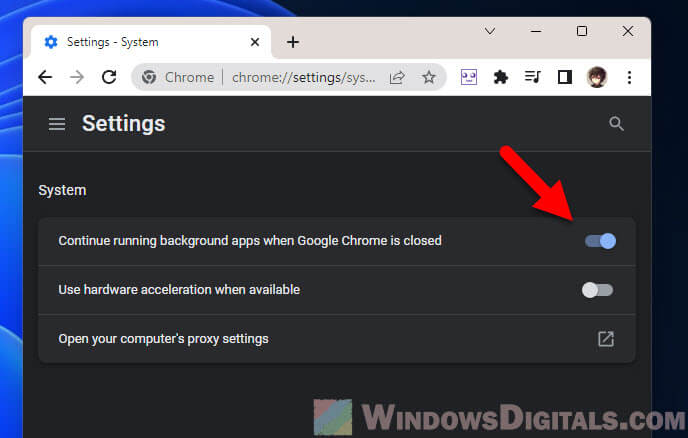
Disable Chrome’s background apps when Chrome is closed
Chrome can keep apps running even when it’s closed. Turning this off stops those background processes.
To do this:
- Go to Chrome’s settings.
- Click on “System” on the left.
- Turn off “Continue running background apps when Google Chrome is closed“.
Also see: How to know which app is using the internet in Windows 11
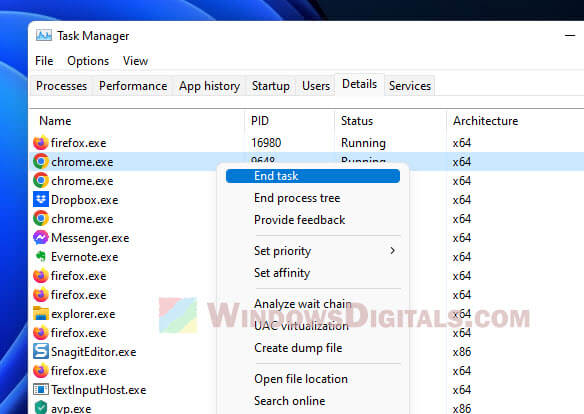
Kill the chrome.exe processes yourself
If you want more control, you can close Chrome processes yourself using the Task Manager or Chrome’s own task manager. This can free up resources.
- Windows 11/10 Task Manager: Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc, find the chrome.exe processes you want to end, and click “End task“.
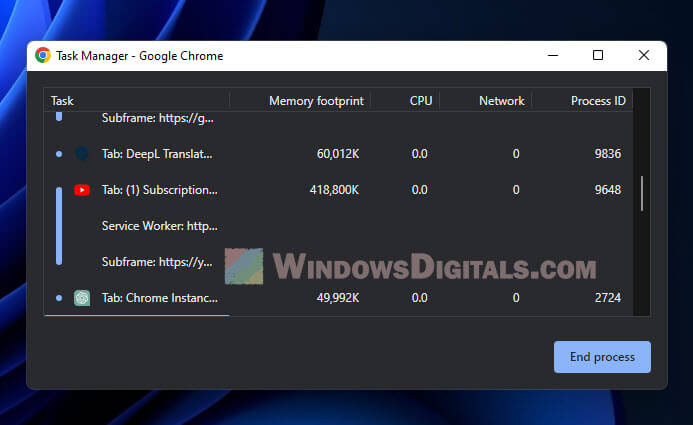
- Chrome Task Manager: Press Shift+Esc, find the processes to close, and click “End process“.
Force Chrome to display a single process
This advanced trick makes Chrome run all tabs in one process, cutting down on instances. But it might make Chrome less stable and safe, so be careful.
To do this:
- Right-click the Chrome shortcut.
- Choose “Properties“.
- Add
--process-per-siteto the end of the “Target” field.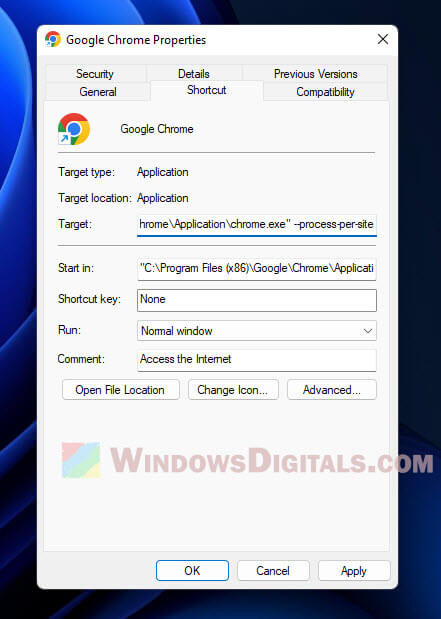
This works for both Windows 11 and Windows 10.
Chrome not opening, but multiple processes running in Task Manager
If Chrome won’t open but you see lots of processes for it, try these steps:
- Kill all Chrome processes in Task Manager and try opening it again.
- If that doesn’t work, restart your computer.
- Clear Chrome’s cache and cookies.
- If still no luck, reinstall Chrome without old settings and extensions.
Chrome’s impact on battery life
Chrome can drain up your battery fast, especially when you have too many tabs open and multiple media processes running at the same time. If you want to reduce some burdens on your device’s battery, lower the number of tabs open and only use extensions that you absolutely need. You can also try out the battery saver mode that comes with Chrome. It will stop background activities that you’re not using at the moment to save you some battery.
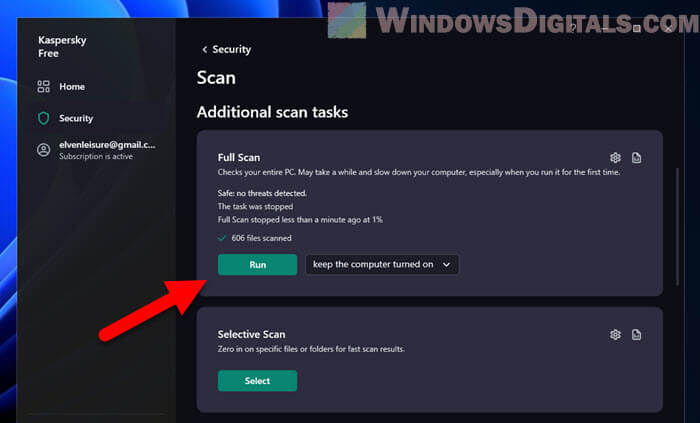
Check for malware and unwanted software
If your computer has malware or software you don’t want, it can make Chrome run a lot of processes, which slows things down. Running a deep scan with software you trust for fighting viruses or malware can help. It can find and get rid of anything bad that’s causing issues.
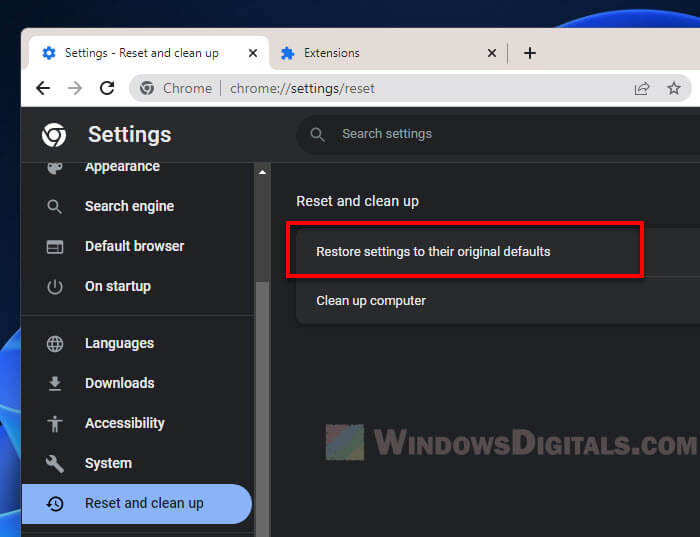
Reset Chrome settings to default
If nothing else works and Chrome is still running too many processes, you might want to reset its settings to how they were at the start. This can solve problems by getting rid of any changes that were causing issues. But be careful—this means you’ll lose any extensions and custom settings you’ve added, so think of it as something to try only if you really need to.
Some final words
Seeing many chrome.exe processes is normal and part of how Chrome works. Though they use some CPU and RAM, it’s meant to make Chrome run better. If you’re worrying about resource usage or battery life, you can follow the tips mentioned in this guide to close some unused tabs, reduce the number of active extensions, stop some background apps, etc. to cut down on Chrome’s processes.